- Home
- Products
- JUVIAGEL – Vaginal moisturizing gel
- MOMAID – After delivery supplement for postpartum recovery
- PROTECTA – Anti-inflammatory skin cream
- INCOXIL – Incontinence dietary supplement
- VITAPHASE– Special dietary supplement adjusted to the phases of the menstrual cycle
- CORTEXIUM – Addressing cognitive challenges in pre-and post-menopausal women
- Pipeline
- Company


At a glance
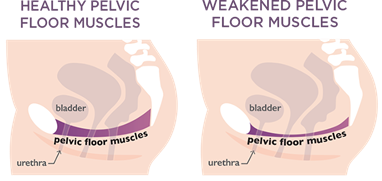
The European Association of Urology (EAU) recommends supervised pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) as first-line therapy for all women with stress or mixed urinary incontinence. To increase the effectiveness of PFMT, we have developed Incoxil, a special dietary supplement based on clinical trial results:
- It significantly increases vaginal squeeze pressure, pelvic floor biomechanical integrity (BI-score), and reduces PGI-S score changes compared to the control group.
- Improvement was observed in almost all parameters tested in the therapeutic group compared to baseline, including urinary incontinence questionnaires (UDI-6, IIQ-7, PGI-S), pelvic floor biomechanical integrity (BI-score), and maximal vaginal squeeze pressure.
Incoxil is a dietary supplement for stronger pelvic floor muscles and less urinary incontinence symptoms.
Medical need
Approximately 50% of women will experience some form of urinary incontinence (UI) in their lifetime, as prevalence and age are positively correlated. UI is a significant economic burden, with annual cost estimates of $19.5 billion or more.
Incontinence can strain social relationships, ruin leisure activities, and impair the performance of incontinent patients to a similar extent as those suffering from asthma or rheumatoid arthritis.
The demand for care of pelvic floor disorders is expected to increase approximately 35% between 2010 and 2030.
Close to 400,000 surgeries are performed in the US
11% lifetime risk for undergoing prolapse or incontinence surgery and 30% will undergo a second surgery.
Market situation
It is difficult to provide an exact number of urinary incontinence patients worldwide because many cases go unreported or undiagnosed. However, according to the International Continence Society, it is estimated that up to 200 million people worldwide are affected by urinary incontinence. It is more common in women than men, and the prevalence increases with age. It is important to note that this is just an estimate and the actual number of individuals affected by urinary incontinence may be higher.
Currently no existing dietary supplements in the market effectively targeting urinary incontinence. There is a clear gap on the market which Incoxil can fill.
Efficacy of Incoxil
In 2022 we have conducted a Randomized Clinical Trial to Assess the Effectiveness of Incoxil Food Supplement and Pelvic Floor Muscle Training in Women With Stress Dominant Urinary Incontinence. (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05358769)
Our results showed that women with stress predominant urinary incontinence receiving a specially formulated supplement in addition to daily pelvic floor muscle training for six weeks had significantly greater strengthening in vaginal squeeze pressure, greater improvement in the Biomechanical Integrity Score and larger decrease in PGI S score compared to control while no statistical difference was found in UDI 6 scores Women in the treatment group on average improved twice as much in their BI score as women in the control group.
Also women with stress predominant urinary incontinence receiving a specially formulated supplement (Incoxil) in addition to daily pelvic floor muscle exercise for six weeks had improved urinary incontinence symptoms compared to their baseline.
- Significantly improved urinary incontinence symptoms (significant decrease in UDI 6 score and IIQ 7), UDI 6 > MICD of 11 points
- BI score improved significantly (on average improved twice as much as women in the control group)
- PGI S scores improved significantly.
- Significantly stronger vaginal squeeze pressure
- Significantly improved Oxford scale on vaginal palpation
Safety of Incoxil
During the clinical testing there were no side effects reported at recommended doses.
Incoxil is manufactured in a GMP complying factory and the whole product lifecycle is managed under ISO 22000.
Science behind Incoxil
Creatine is a non-essential nitrogenous organic acid that occurs in vertebrates, and it is also synthesized in the human body from L arginine, glycine and L methionine. Approximately 95 of the creatine pool in the body is located in skeletal muscle
MOA: increase of the creatine phosphate pool in muscle cells following daily consumption of creatine can enhance the ATP regeneration rate after intense muscle contractions.
Creatine consumption in combination with resistance training improves the muscle’s ability to train at higher intensities and this leads to higher muscle strength.
Consumed at doses of at least 3 g/day in combination with regular resistance training (three times per week for several weeks) of moderate intensity, improves on muscle strength in adults over the age of 55.
Product details
Tasteless instant drink powder containing 28 daily doses, packaged in daily sachets.
Ingredients: Creatine (3000mg), Leucine (500mg), Calcium (120mg), Magnesium (60mg), Zinc (5mg).
Directions for use: Mix one sachet of beverage powder in 2 cups of water or other liquid. One sachet per day is recommended immediately after pelvic floor exercises.
Shelf life: 36 months after production.